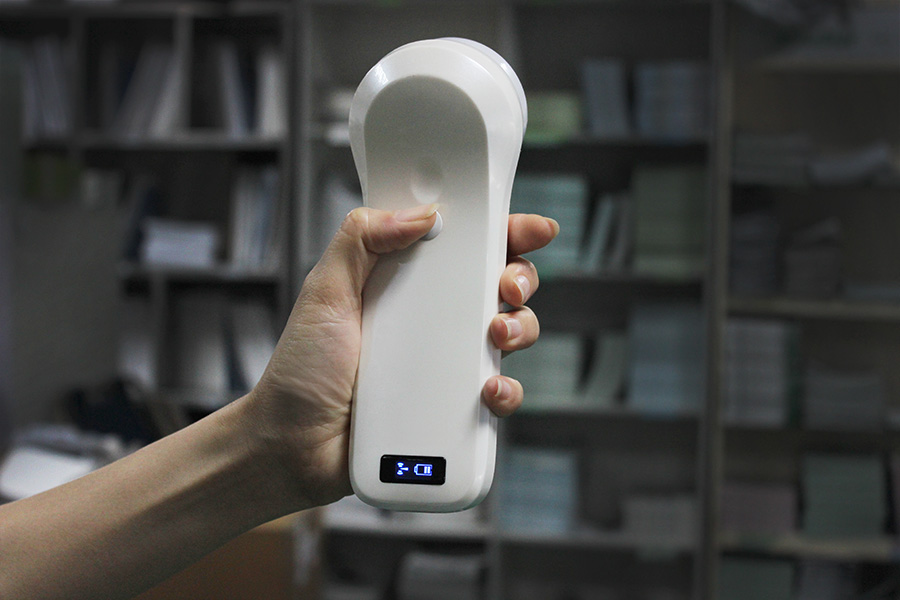
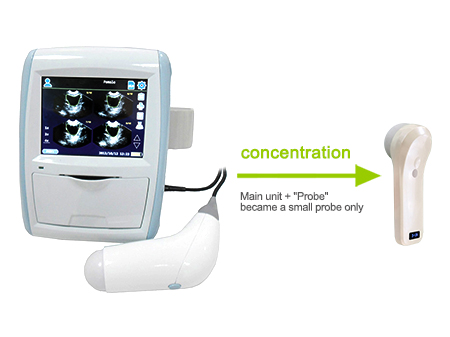
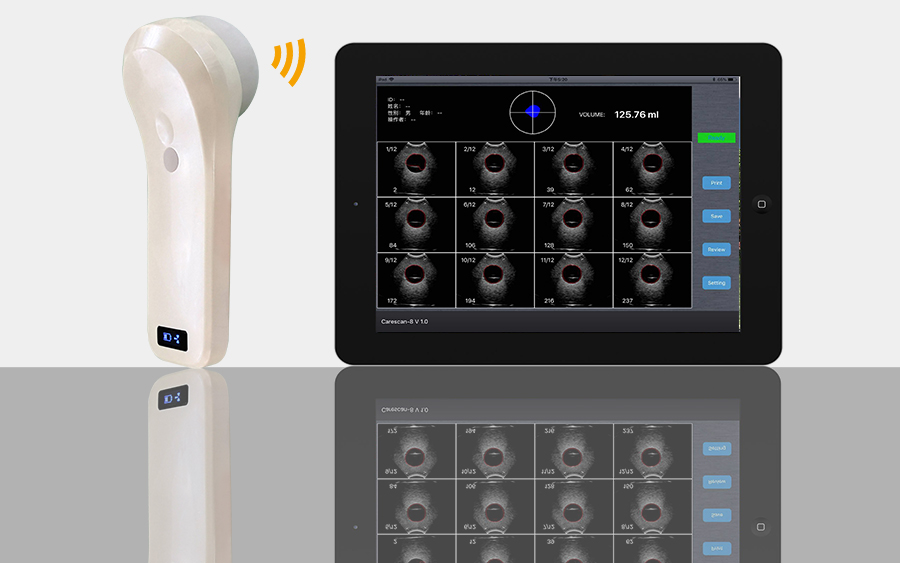


How it works
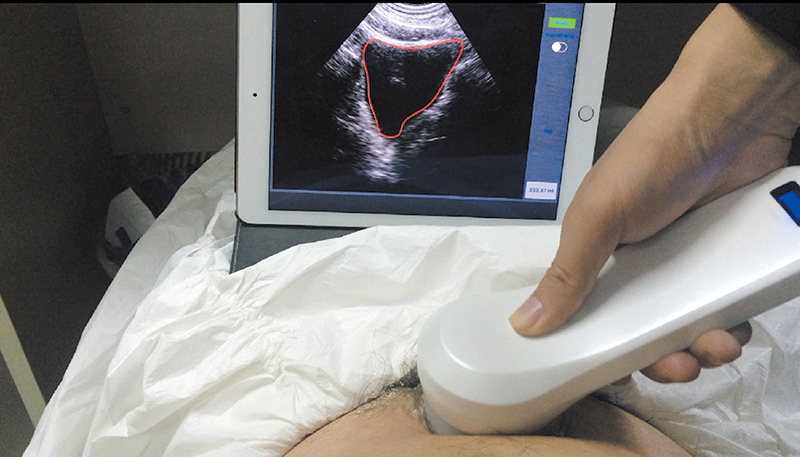
The Sonostar wireless probe is a mini ultrasound scanner without a screen. We minimize the components of a traditional ultrasound into a small circuit board built into the probe, and showing image in smart phone/tablet through Wifi transferring. image can both show in screen and tablet.Image transferring through internal wifi from probe, no need external Wifi signal.
Advantage
- Only one probe, convenient for carry
- Wireless, convenient for operation
- 4D array scan, very clear image
- High accurate (5% inaccuracies)
- High speed on scan and process (2s)
- Without distortion of mechanical scanning
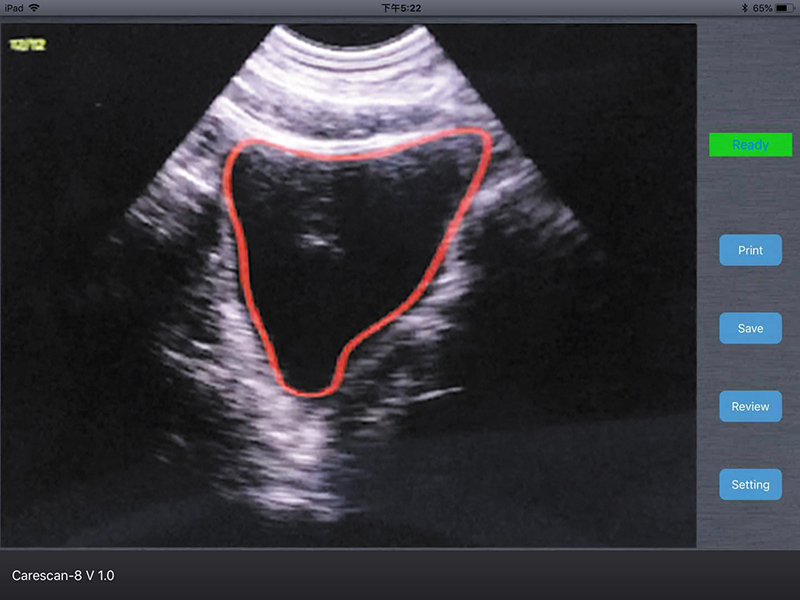
- More advanced algorithm, more powerful bladder wall recognition technology(High recognition rate for the bladder wall with air), more accurate contour technology, higher accuracy of the probe makes scanning results more accurate.
- New algorithm, the measurement results are not subject to the bladder shape and size.
No need to select Gender, Age group and no need to consider special cases such as the effect of hysterectomy on the measurement results. Good compatibility for different bladders, no Ubstantial error when measuring small volume or special shape bladders, easier to operate and use.
- High precision rotary encoder, precise positioning, never need to calibration.
- Waterproof probe
Specifications
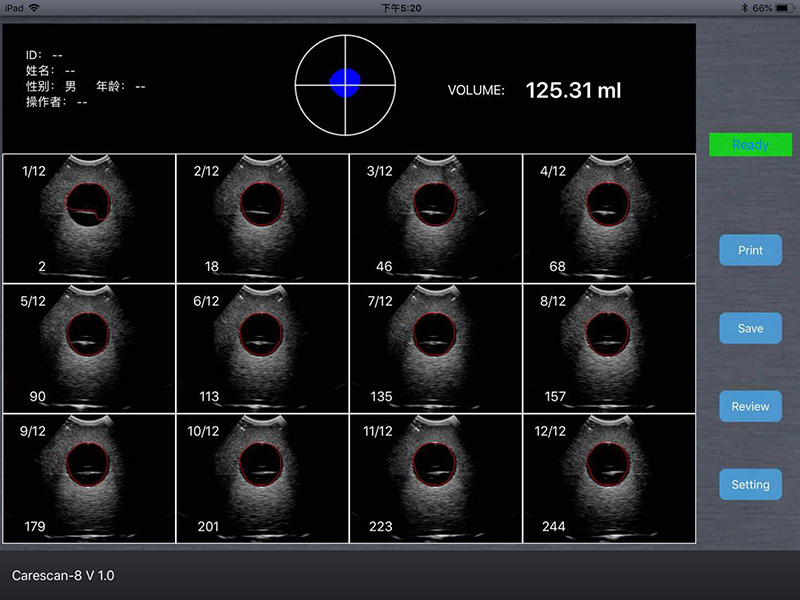
1. Scan mode: array probe, 4D scan;
2. Supporting system: Apple iOS;
3. Measuring range: 10ml ~ 2000ml;
4. Automatic measurement inaccuracies: <5%;
5. Scan and process<2 seconds;
6. Scanned image display frame: 10 frames / seconds;
7. Case Storage: by tablet or mobile phone;
8. Printing: external wireless thermal printer;
9. Battery: Built-in battery, charge one time can work on more than 200 patients;
10. Power: Wireless charge or by USB cable charge;
11. Dimension: 180mm (length) × 60mm (width) × 60mm (thickness);
12. Weight: 420g.
13.Battery working time: 3 hours(according to whether keep scan)
Applications
1. Urology: Determine the degree of acute and chronic urinary retention, and determine the timing of catheterization and surgery; Neuromodulation was used to judge the effect of regulation after operation; Determination of the degree of urethral obstruction or prostate hyperplasia.
2. Obstetrics: Postpartum stress urinary incontinence; Determine the degree of postpartum pelvic floor muscle damage.
3. Gynecology: Determine the degree of pelvic floor neuromuscular injury after pelvic tumor surgery, and determine the surgical or rehabilitation therapy plan. 4. Severe ICU: Determining the timing of intermittent catheterization for patients with long-term indwelling catheters, reducing the frequency of catheterization, reducing the risk of infection, and helping patients recover from spontaneous urination.
5. Neurology department: to determine the damage degree of detrusor and sphincter in patients with neurogenic bladder.
6. Nursing: For patients with indwelling catheters after surgery, it is used to determine the timing of catheter removal, reduce the duration of catheter retention, and reduce the risk of infection.
7. Rehabilitation department: monitoring the effectiveness of pelvic floor rehabilitation treatment; Develop a training plan for bladder retraining and rehabilitation treatment, providing a basis for the degree of bladder function recovery.
8. Emergency Department: Diagnosis of acute urinary pig retention patients and guidance for urinary catheterization; Acute trauma is used to determine whether a patient's bladder is damaged or ruptured.
9. Radiotherapy department: Used to determine bladder function during radiotherapy for patients with pelvic floor tumors or bladder tumors.

 关注微信公众号
关注微信公众号
 加微信咨询
加微信咨询

